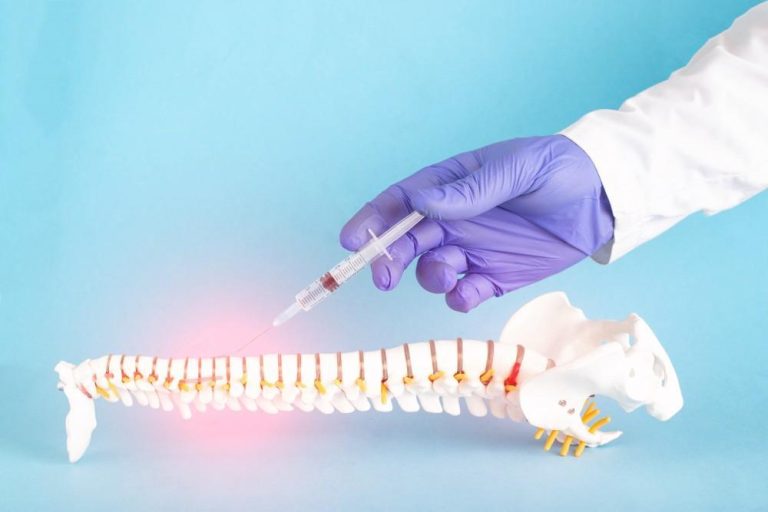
Inflammation in back pain plays a critical role, often being the underlying cause of chronic discomfort. Whether due to poor lifestyle habits, underlying health conditions, or external factors, inflammation can lead to persistent spinal issues. Understanding the connection between inflammation and back pain is key to finding relief and preventing long-term damage.
In this guide, we’ll explore how inflammation contributes to back pain, common pain triggers, and the best anti-inflammatory treatments to help you maintain a healthy spine.
How Inflammation Contributes to Back Pain
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism, responding to injury or irritation by increasing blood flow and immune activity. While acute inflammation helps in healing, chronic inflammation can lead to prolonged pain and tissue damage, especially in the spine.
- Inflammatory Response: When muscles, ligaments, or spinal discs are injured, the body triggers an immune response that may cause swelling and pain.
- Chronic Conditions: Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis often cause long-term spinal inflammation.
- Nerve Irritation: Inflammatory chemicals can irritate spinal nerves, leading to sciatica and other nerve-related pain.
For more insights into inflammation-related spinal conditions, check out this Johns Hopkins guide on back pain.
Common Pain Triggers: Foods, Lifestyle, and More
Many daily habits contribute to chronic inflammation and back pain. Identifying and eliminating these pain triggers can significantly improve spine health.
1. Pro-Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, worsening back pain. These include:
- Processed sugars (soda, candy, baked goods)
- Trans fats (fast food, fried items)
- Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pasta)
- Excessive alcohol and red meat
2. Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of movement leads to poor circulation and stiffness, aggravating inflammation. Sitting for prolonged hours, especially with bad posture, puts excessive strain on the lower back and spine.
3. Poor Posture and Ergonomics
Incorrect sitting positions and improper workstation setups can create chronic tension in the back. An ergonomic workspace with proper chair support and screen height adjustments reduces inflammation-related strain.
4. Stress and Cortisol
Chronic stress increases cortisol levels, which can heighten inflammatory responses in the body. Engaging in stress management techniques can help in reducing inflammation-related back pain.
For a deeper look into how stress impacts pain, read this Healthline article on stress and back pain.
Best Anti-Inflammatory Solutions for Back Pain
Managing chronic inflammation requires a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary improvements, and medical treatments.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can reduce pain and swelling naturally:
- Omega-3 fatty acids (salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, broccoli)
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries, raspberries)
- Turmeric & Ginger (natural anti-inflammatory properties)
2. Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in low-impact exercises like yoga, swimming, and walking can improve spinal flexibility and reduce inflammation. Strengthening core muscles provides better spinal support.
3. Medications & Natural Supplements
- NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen) help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Turmeric supplements contain curcumin, a powerful natural anti-inflammatory agent.
- Vitamin D & Magnesium support bone and muscle health, reducing inflammatory responses.
When to Seek Professional Help
If back pain persists for more than a few weeks, or worsens despite home remedies, it’s crucial to consult a specialist. Warning signs include:
- Persistent morning stiffness
- Radiating pain to the legs or arms
- Unexplained weight loss along with back pain
- Difficulty standing or walking
A spine specialist can determine if your pain is due to chronic inflammation or another underlying condition.
ASAP’s Approach to Inflammatory Back Pain Treatment
At Advanced Spine and Pain (ASAP), we specialize in non-surgical and minimally invasive treatments that target inflammation and relieve back pain.
Our Treatment Options:
- Epidural Steroid Injections (ESIs): Reduce inflammation around spinal nerves.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: Uses natural healing properties to repair tissue damage.
- Physical Therapy & Chiropractic Care: Strengthen muscles and improve spinal alignment.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Advanced techniques for long-term pain relief.
Schedule a consultation with our ASAP pain management team to develop a customized treatment plan.
Conclusion
Inflammation in back pain is a common yet treatable issue. Identifying pain triggers, making dietary and lifestyle changes, and seeking medical care when needed can significantly reduce discomfort and improve spine health.
If you’re experiencing chronic back pain, don’t wait for it to worsen. Contact ASAP today to explore personalized solutions for inflammation-related spinal conditions.